The full spelling of MOS FET is Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor.
It is the structure which stacked up Metal, Oxide and Semiconductor.
There are NPN type and PNP type as the semiconductor part. NPN type is called N-channel and PNP type is called P channel. An oxide film is put to the semiconductor of NPN or PNP and metal is put onto it as the gate. In case of NPN, the part of "N" is a source pole and a drain pole. In case of PNP, the part of "P" are the poles.
Transistor controls an output current by the input current. However, in case of FET, it controls an output current by input voltage(Electric field). The input current doesn't flow.
To handle an MOS FET, it needs an attention. Because the oxidation insulation film is thin, this film is easy to destroy in the high voltage of the static electricity and so on.

 The operation principle of P-N junction diode The operation principle of P-N junction diode
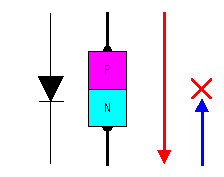
First of all, I will explain about the operation principle of P-N junction diode simply.
The N-type semiconductor has Electrons(Negative) and the P-type semiconductor has Electron holes(Positive).
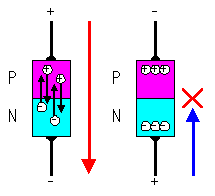
When the positive voltage to the side of P-type and the negative voltage to the side of N-type are applied respectively, the electron in N-type is pulled with the positive voltage on the side of P-type and the electron flows through to the P-type beyond the boundary of the semiconductor. Also, the hole in P-tyep is pulled with the negative voltage on the side of N-type and the hole flows through to the N-type. In this way, the electric current flows through the semiconductor.
As the opposite case, when the positive voltage to N-type and the negative voltage to P-type are applied respectively, the electron in N-type is pulled with the positive voltage on the side of N-type and the hole in the P-type is pulled with the negative voltage on the side of P-type. In this case, the electron in the semiconductor doesn't move through the boundary and the electric current doesn't flow.

 The operation principle of MOS FET The operation principle of MOS FET
The semiconductor part of MOS FET consists of NPN or PNP. So, when not applying voltage to the gate, the electric current doesn't flow between drain and source.
When positive voltage is applied to the gate of the N-channel MOS FET, the electrons of N-channel of source and drain are attracted to the gate and go into the P-channel semiconductor among both. With the move of these electrons, it becomes the condition like spans a bridge for electrons between drain and source. The size of this bridge is controlled by the voltage to apply to the gate.
In case of P-channel MOS FET, the voltage is opposite but does similar operation. When negaive voltage is applied to the gate of P-channel MOS FET, the holes of P-channel of source and drain are attracted to the gate and go into the N-channel semiconductor among bith. With the move of these holes, a bridge for holes is spaned and the electric current flows between drain and source.
Because there is an oxide film between gate and semiconductor, the electric current doesn't flow through the gate. An electric current flow between drain and source is controlled only with the voltage which is applied to the gate.

 The operation principle of C-MOS FET The operation principle of C-MOS FET
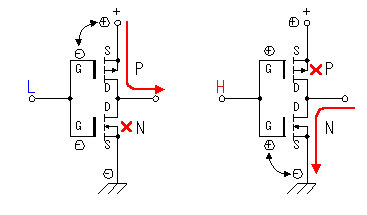 C-MOS FET is the abbreviation of Complementary MOS FET. C-MOS FET is the circuit which combined a P-channel MOSFET and a N-channel MOSFET. When the input is an L level, the P-MOS FET becomes ON condition and when the input is H level, the N-MOS FET becomes ON condition. At the C-MOS FET circuit, the N-MOS FET and the P-MOS FET do the operation which is always opposite. C-MOS FET is the abbreviation of Complementary MOS FET. C-MOS FET is the circuit which combined a P-channel MOSFET and a N-channel MOSFET. When the input is an L level, the P-MOS FET becomes ON condition and when the input is H level, the N-MOS FET becomes ON condition. At the C-MOS FET circuit, the N-MOS FET and the P-MOS FET do the operation which is always opposite.
The important characteristic of this circuit is that the comparatively big output current can be controlled. When the input becomes an L level, the output is connected with the power supply by the P-MOS FET and becomes H level. Also, when the input becomes H level, the output is connected with the grounding by the N-MOS FET and becomes an L level. Phase of the input and the output is opposite.
The drain current of MOS FET is cut off even if the gate voltage doesn't become 0 V. It may depend on the kind of the FET but a drain current is cut off when the gate voltage is lower than 1V or 2V. So, in case of C-MOS circuit, P-MOS FET and N-MOS FET don't become ON condition at the same time.
 |