(MB87014A)
 Block diagram of the top is a clickable image map. You can jump to each page of the explanation when you click each block. |
 |  |
|
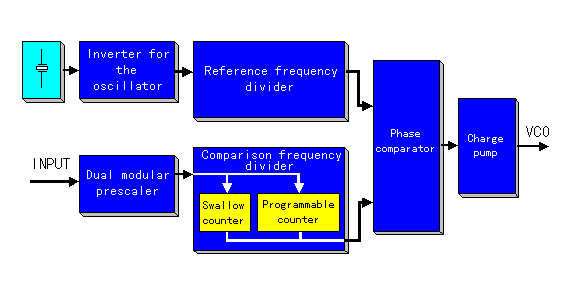
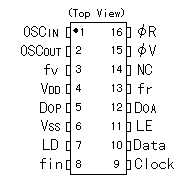
MB87014A is the IC for the PLL synthesizer which was made with CMOS. The shape is SMT(Surface Mount Type) in DIP(Dual In Line Package) of 16pins. This IC is composed of the following functional block.
The operation possible frequency is to 180 MHz in the specification. The singular point of this IC is to use serial data to specify the dividing ratio of the reference frequency divider and the comparison frequency divider. This singular point is good because it can rarely do the IC number of pin but the serial data generation circuit which specifies a dividing ratio becomes necessary. It may be that there is dividing ratio setting IC or a circuit for this IC. Because the PLL to introduce this time is the purpose to output the frequency of the fixation, it is made to make serial data with the initialization circuit as the initial setting operation in case of the turning on. Because it composed in the general logic ICs, it became a comparatively big circuit. At the actual printed board, most are the space of this initialization circuit.
 It is the one to have installed a pole in the crystal to have made shaped like the board thin. The frequency is decided by the thickness of the crystal board. It is possible to make oscillate a specific frequency by the stability.
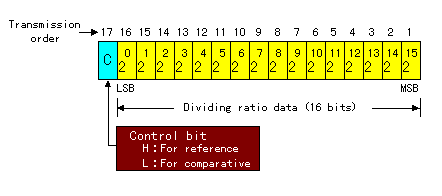
It specifies a dividing ratio by 16 bits as mentioned above both for the reference frequency divider and the comparison frequency divider. However, the handling differs in the reference frequency divider and the comparison frequency divider.
The specification range is possible to 5 - 65535.
It handles 20-25 6 bits with the swallow counter and it handles 26-215 with the programmable counter. It is a specification range below each.
Because it is, the range where the comparative divider can be specified becomes by 320 - 65535.
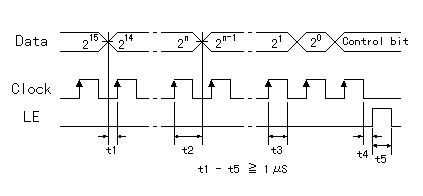
Data is read at the time of the rise of Clock. When the LE is H level, Data part is read by the appropriate counter. When the control bit in the Data part is H, it becomes data for the reference frequency divider and in case of the L, it becomes data for the comparison frequency divider.
This condition is canceled when specifying data except "all zero".
The output of the inverter is returned to the input of the inverter through the crystal oscillator. By this, it makes do the oscillation which was stable at the natural frequency of the crystal oscillator.
10 bits of higher ranks of the dividing ratio setting data (16 bits) are used as the set value of the programmable counter.
The relation of the output of each input frequency and phase comparator and charge pump becomes like the following figure. 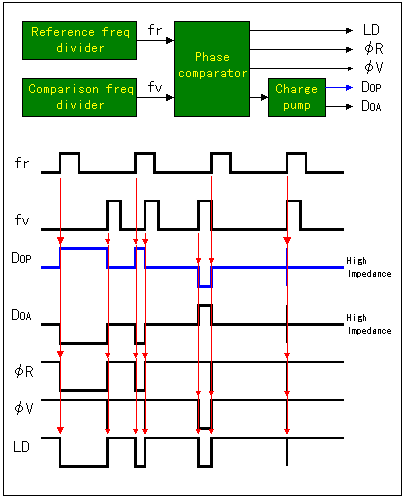 There are five kinds pieces of output. The circuit this time is using DOP output for the passive lowpass filter. As for this output, when fv is low (the period is long), the positive signal which accepted a fimite difference is output by DOP. It is using a varicap diode for the frequency adjustment by VCO to be explaining in the circuit explanation of the VCO. The capacitance of the diode becomes small when the voltage becomes high. Because it is, the capacity of the varicap becomes small when the voltage which is output from DOP becomes positive and the oscillation frequency of the VCO becomes high. When fv is high (the period is short), the negative signal which accepted a fimite difference is output by DOP. The voltage which is gained by the varicap by this becomes low and the capacity of the varicap becomes big. Because it is, the oscillation frequency of the VCO becomes low. The control of the oscillation frequency of the VCO is done in this way.
Because it is, it works in the condition of fr > fv.
It outputs below by the relation in reference frequency (fr) and comparison frequency (fv).
The result of the phase comparator is directly output by LD terminal (7th pin). The output contents are as follows.
|